California's Central Valley
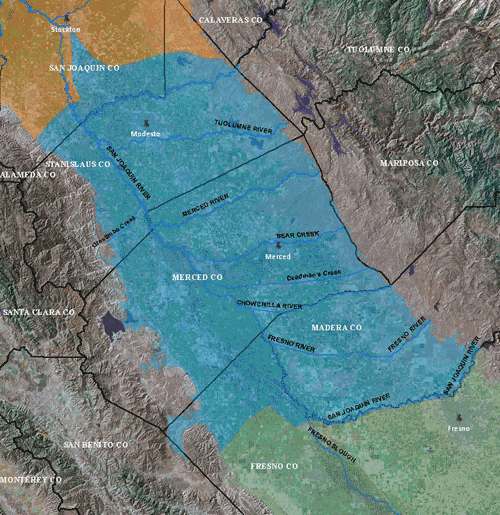
The Central Valley: San Joaquin Basin
Population
The total population of the San Joaquin Basin in 2000 was approximately 2 million (Great Valley Center, 2005).
Major Cities
Stockton, Turlock, Merced, and Modesto
Geographic Features
San Joaquin, Stanislaus, Tuolumne, and Merced Rivers, and the southern part of the Delta
Climate
The San Joaquin Basin has mild winters and particularly hot and dry summers.
Land Use
A large part of the population of the basin is involved in all facets of agricultural production. Gradually, the population is shifting towards supporting the large urban areas and industry.
In 2000, approximately 2/3 of the area was used for agriculture. The southwestern half of the San Joaquin Basin has long been known for its cotton fields, but recent drops in cotton prices have caused a rapid shift to other crops, particularly almond orchards. On the eastern side of the San Joaquin Basin, alluvial fans are dominated by deciduous fruit and nut orchards. The remainder of the irrigated area is covered by pasture, truck, and field crops.
Water Use
Although surface water is used when it is available, the region relies heavily on groundwater. Groundwater accounts for about 30% of the annual supply of both types of water used for agricultural and urban purposes (California Department of Water Resources, 2003; Chapter C).Only about 8% of the historic San Joaquin Valley wetland acreage remains today (Moore and others, 1990).
